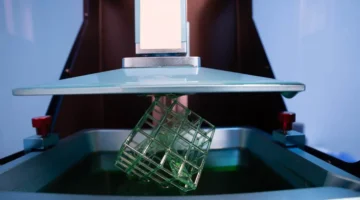
Resin vs. Filament (PLA/FDM): Understanding the Core Differences
(Targets: 3d print resin vs filament, 3d print resin vs pla, 3d print resin vs fdm)
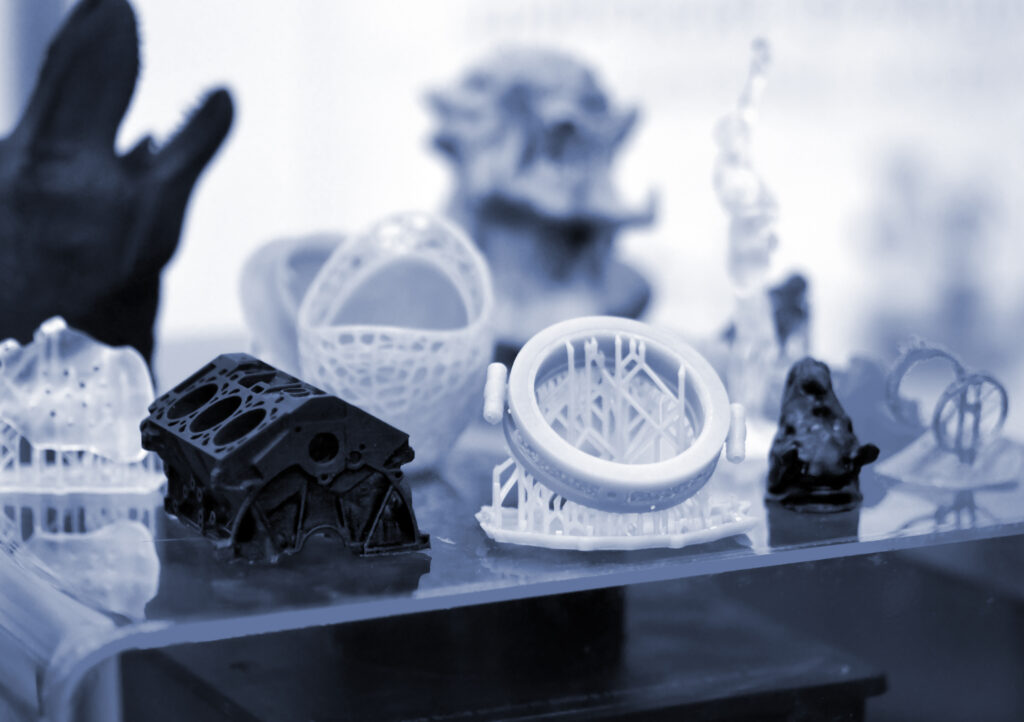
When deciding between resin and filament for 3D printing, it’s important to understand the fundamental differences in print quality, applications, and overall performance.
| Feature | Resin (SLA/DLP/LCD) | Filament (FDM/PLA/ABS) |
|---|---|---|
| Print Resolution | Ultra-high detail (25–50 microns) | Moderate detail (100–300 microns) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, almost injection-mold quality | Visible layer lines, requires sanding |
| Strength & Durability | Excellent mechanical properties (depends on resin type) | Tough, but weaker layer adhesion |
| Cost | Resin slightly more expensive | Filament usually lower cost |
| Applications | Jewelry, dental, engineering prototypes, casting | Prototypes, large mechanical parts, hobby printing |
When to Choose Resin
- Precision and fine details (jewelry, dental, models).
- Smooth finish and complex geometries.
- Applications needing biocompatibility or specialized properties.
When to Choose Filament
- Larger parts at lower cost.
- Simple functional prototypes.
- Quick, low-cost prototyping without specialized equipment.
Casting Resins: The Ultimate Solution for Jewelry and Industrial Molds
(Targets: 3d print resin for jewelry, 3d print resin molds)
Resin is the gold standard for casting applications. With specially formulated castable resins, you can achieve clean burnout, low ash residue, and flawless surface detail.
For jewelry and precision industrial parts, resins like Resinify CleanCast, JewelCast, and WaxCast are optimized to replicate every fine detail.
👉 For flawless results in investment casting, explore our line of high-detail castable jewelry resins (link to Jewelry Category).
Can You 3D Print Resin Molds? (YES — Here’s How)
(Targets: can you 3d print resin molds)
Yes, you can! While resins are not typically used as the mold material itself, they are used to print master patterns. These masters can then be used to:
- Create silicone molds for mass duplication.
- Burn out cleanly in investment casting for metal jewelry and dental applications.
- Produce prototypes with extreme accuracy before committing to traditional mold-making.
Selecting Resins for Extreme Environments
(Targets: 3d print resin heat resistance, 3d print resin for outdoor use)
Not all resins are equal — some are engineered for high heat, chemical resistance, and outdoor durability.
At Resinify, we’ve developed engineering-grade resins like:
- ResinMax™ – A high-temp resin built for industrial environments.
- CeramicTough™ – Designed for superior mechanical performance.
👉 If you require high-temperature tolerance, consider using our ResinMax high-temp engineering resin (link to ResinMax product page).
Is Resin Toxic? Safe Handling and Disposal Practices
(Targets: is 3d print resin toxic, 3d print resin safety)
A common question is: “Is 3D print resin toxic?”
The short answer: Uncured resin requires careful handling, but cured resin is safe.
Safe Handling Guidelines
- Always wear gloves, safety glasses, and a lab coat when working with liquid resin.
- Work in a well-ventilated area or use an air purifier.
- Use isopropyl alcohol (IPA) or approved cleaners to wash prints.
- Fully cure parts with a UV curing unit before use.
👉 For more details on proper handling, see our Ultimate Guide to Post-Processing 3D Prints (link to first article).
Conclusion: Resin or Filament — Which Should You Choose?
- Choose resin if you need precision, smooth surfaces, and specialized materials (jewelry, dental, engineering).
- Choose filament if you need quick, low-cost, large functional prototypes.
With Resinify’s advanced resin formulations, you can take advantage of next-gen materials designed for professional workflows across dentistry, jewelry casting, and industrial prototyping.
Quick Q&A Section (for SEO snippets)
Q: Can you 3D print resin molds?
A: Yes — resin is used to print master patterns that can be used in silicone or investment casting molds.
Q: Is resin stronger than filament?
A: In many cases, yes. Specialized resins offer higher strength, toughness, and wear resistance than PLA or ABS filament.
Q: Is 3D print resin toxic?
A: Uncured resin must be handled carefully with PPE. Once cured, it is safe for dental, jewelry, and engineering applications.
Q: What is resin best used for?
A: Resin is best for high-detail, precision applications like dental prosthetics, jewelry casting, and industrial prototypes.