📝 Pillar Article Draft – Ready for WordPress
Title (H1):
👉 The Ultimate Guide to Resin 3D Printing: Settings, Curing, and Post-Processing
Introduction
Resin 3D printing has become one of the most powerful tools for producing highly detailed, functional, and esthetic parts. Whether you’re a dental professional, jeweler, or product engineer, resin printing provides accuracy and finish quality unmatched by FDM/filament printing.
This comprehensive guide explains how to 3D print with resin step by step, covering printer setup, printing parameters, cleaning, curing, and safety. Along the way, we’ll link to advanced resins engineered for specific applications like Dental Resins, Jewelry Casting Resins, and Engineering Resins.
1. Preparing for Resin 3D Printing
Printer Setup:
- Ensure your printer is level and calibrated. A misaligned build plate causes poor adhesion.
- Mix the resin bottle well before pouring (sediment can settle).
- Fill the resin vat just above the minimum line.
Environmental Conditions:
- Resin performs best at 20–25 °C (68–77 °F).
- If resin is too cold, it becomes viscous and may not cure properly. Warm resin slightly before printing.
- Always keep dust and stray UV light away from your workspace.
👉 For dental labs, resins like BasePro™ Denture Base are sensitive to storage temperature—keep bottles sealed and stored properly.
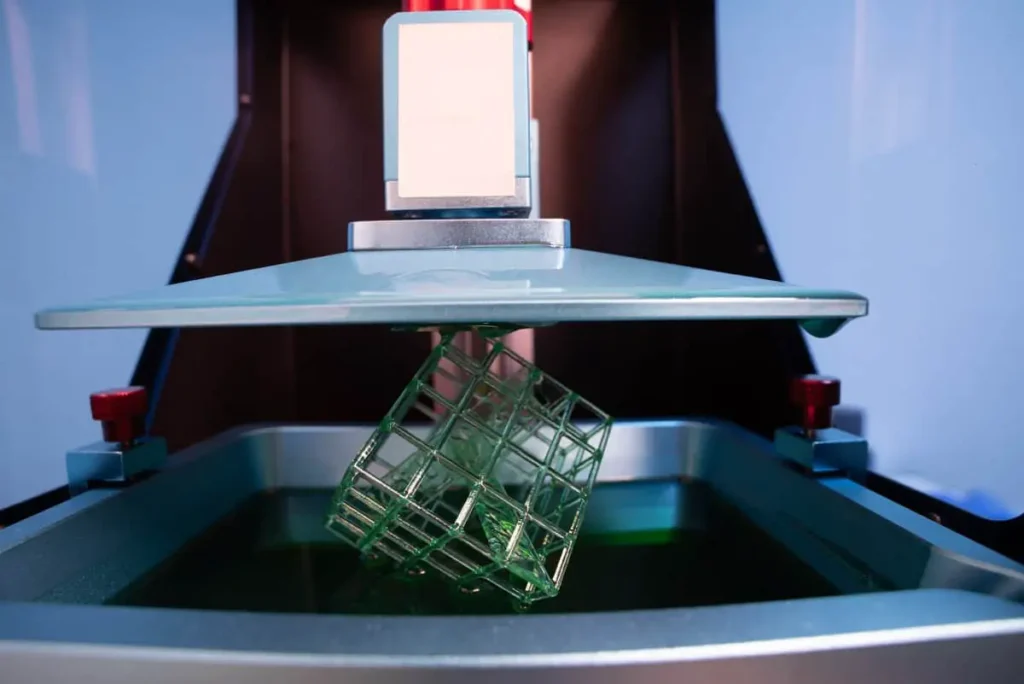
2. Printing with Resin
Resin printing works by curing liquid resin layer by layer using UV light (385–405 nm). Getting the right settings is crucial.
Key Printing Parameters:
- Layer Height: Standard = 50 µm, High detail = 25 µm, Fast prints = 100 µm.
- Bottom Layers: 4–6 layers with longer exposure (30–40 sec).
- Normal Exposure Time: 2–4 sec per layer (varies by resin).
- Supports: Always enable for overhangs—resin prints need structural support.
👉 For crown and bridge accuracy, CrownPro™ Dental Resin performs best at 25–50 µm layer heights for precise fit.
3. Cleaning and Handling Prints
Once the print is complete, carefully remove it from the build plate. Resin at this stage is still uncured and toxic, so handle with gloves.
Washing Steps:
- Rinse the part in >96% IPA (isopropyl alcohol) or resin cleaner.
- Use an ultrasonic cleaner or agitation for better results.
- Wash for 3–5 minutes; avoid over-soaking (can weaken parts).
- Air dry or use compressed air.
👉 Jewelry casters prefer WaxCast™ or CleanCast™ since they wash clean and leave zero ash during burnout.
4. Post-Curing Resin Prints
Post-curing strengthens resin parts and ensures biocompatibility for dental resins.
Why Curing Matters:
- Increases hardness and strength.
- Improves heat and wear resistance.
- Prevents tacky surfaces caused by oxygen inhibition.
Curing Guidelines:
- Temperature: 60–65 °C for dental/engineering resins.
- Time: 20–25 minutes.
- Light: Use a 385–405 nm curing unit (Otoflash, CUREbox, Dreve PCU LED).
👉 Example: ResinMax Engineering Resin reaches peak toughness after a full post-cure cycle.
5. Safety and Handling
One of the most-searched questions is: “Is 3D print resin toxic?”
Key Safety Tips:
- Always wear nitrile gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid skin/eye contact. If exposed, wash with soap/water and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Never pour waste resin down the drain—collect and cure before disposal.
- Fully cured resin is generally safe for handling in its intended applications (dental, jewelry, engineering).
👉 Biocompatible dental resins like GuardPro™ Night Guard Resin are tested to ISO 10993 standards for patient safety.
6. Common Questions About Resin 3D Printing
Q: Can you 3D print resin molds?
A: Yes. Engineering resins like ToughMold™ are designed for mold-making and tooling. For metal casting, you 3D print a burnout pattern using resins like WaxCast™, not a reusable mold.
Q: What material is 3D print resin?
A: A blend of photopolymers, photoinitiators, and additives. Resinify resins are specialized for dentistry, jewelry casting, and engineering.
Q: Can you reuse resin?
A: Yes, but always filter resin through a fine mesh after printing to remove cured particles. Store in an opaque container away from light/heat.
Q: How strong is resin compared to filament?
A: Engineering resins like ResinMax and CeramicTough rival or exceed PLA/ABS in tensile and flexural strength.
Q: What is the shelf life of resin?
A: Most resins last 24 months unopened; once opened, use within 6 months.
7. Internal Links for SEO
Throughout the post, link strategically:
- Dental applications → Dental Category Page
- Jewelry burnout → Jewelry Category Page
- Engineering strength → Engineering Category Page
- Individual mentions (BasePro, CrownPro, WaxCast, ResinMax) → product pages
8. Conclusion
Resin 3D printing is no longer limited to hobbyists—it’s now powering breakthroughs in dentistry, jewelry, and engineering. By mastering preparation, printing, cleaning, curing, and safety, you can achieve reliable results every time.
👉 Explore our full range of Resinify 3D Printing Resins to find the right material for your next project.
🔑 SEO Checklist for This Post
- Focus Keyword: how to 3d print resin
- Secondary Keywords: 3d print with resin, 3d print resin settings, resin cure time, is 3d print resin toxic, resin vs filament.
- Word Count: ~1600 (this draft covers it).
- Schema: Add FAQPage + HowTo with Rank Math.
- Internal Links: 3 category pages + 4 product pages.
👉 Do you want me to also format this into a ready-to-paste WordPress blog post (with H2/H3 headings, bullet lists, and FAQ schema blocks marked), so you just drop it into the editor?
The Ultimate Guide to Resin 3D Printing: Settings, Curing, and Post-Processing
Introduction
Resin 3D printing has become one of the most powerful tools for producing highly detailed, functional, and esthetic parts. Whether you’re a dental professional, jeweler, or product engineer, resin printing provides accuracy and finish quality unmatched by FDM/filament printing.
This comprehensive guide explains how to 3D print with resin step by step, covering printer setup, printing parameters, cleaning, curing, and safety. Along the way, we’ll link to advanced resins engineered for specific applications like Dental Resins, Jewelry Casting Resins, and Engineering Resins.
1. Preparing for Resin 3D Printing
Printer Setup:
- Ensure your printer is level and calibrated. A misaligned build plate causes poor adhesion.
- Mix the resin bottle well before pouring (sediment can settle).
- Fill the resin vat just above the minimum line.
Environmental Conditions:
- Resin performs best at 20–25 °C (68–77 °F).
- If resin is too cold, it becomes viscous and may not cure properly. Warm resin slightly before printing.
- Always keep dust and stray UV light away from your workspace.
For dental labs, resins like BasePro™ Denture Base are sensitive to storage temperature—keep bottles sealed and stored properly.
2. Printing with Resin
Resin printing works by curing liquid resin layer by layer using UV light (385–405 nm). Getting the right settings is crucial.
Key Printing Parameters:
- Layer Height: Standard = 50 µm, High detail = 25 µm, Fast prints = 100 µm.
- Bottom Layers: 4–6 layers with longer exposure (30–40 sec).
- Normal Exposure Time: 2–4 sec per layer (varies by resin).
- Supports: Always enable for overhangs—resin prints need structural support.
For crown and bridge accuracy, CrownPro™ Dental Resin performs best at 25–50 µm layer heights for precise fit.
3. Cleaning and Handling Prints
Once the print is complete, carefully remove it from the build plate. Resin at this stage is still uncured and toxic, so handle with gloves.
Washing Steps:
- Rinse the part in >96% IPA (isopropyl alcohol) or resin cleaner.
- Use an ultrasonic cleaner or agitation for better results.
- Wash for 3–5 minutes; avoid over-soaking (can weaken parts).
- Air dry or use compressed air.
Jewelry casters prefer WaxCast™ or CleanCast™ since they wash clean and leave zero ash during burnout.
4. Post-Curing Resin Prints
Post-curing strengthens resin parts and ensures biocompatibility for dental resins.
Why Curing Matters:
- Increases hardness and strength.
- Improves heat and wear resistance.
- Prevents tacky surfaces caused by oxygen inhibition.
Curing Guidelines:
- Temperature: 60–65 °C for dental/engineering resins.
- Time: 20–25 minutes.
- Light: Use a 385–405 nm curing unit (Otoflash, CUREbox, Dreve PCU LED).
Example: ResinMax Engineering Resin reaches peak toughness after a full post-cure cycle.
5. Safety and Handling
One of the most-searched questions is: “Is 3D print resin toxic?”
Key Safety Tips:
- Always wear nitrile gloves, safety glasses, and protective clothing.
- Work in a well-ventilated area.
- Avoid skin/eye contact. If exposed, wash with soap/water and seek medical attention if irritation persists.
- Never pour waste resin down the drain—collect and cure before disposal.
- Fully cured resin is generally safe for handling in its intended applications (dental, jewelry, engineering).
Biocompatible dental resins like GuardPro™ Night Guard Resin are tested to ISO 10993 standards for patient safety.
6. Common Questions About Resin 3D Printing
Q: Can you 3D print resin molds?
A: Yes. Engineering resins like ToughMold™ are designed for mold-making and tooling. For metal casting, you 3D print a burnout pattern using resins like WaxCast™, not a reusable mold.
Q: What material is 3D print resin?
A: A blend of photopolymers, photoinitiators, and additives. Resinify resins are specialized for dentistry, jewelry casting, and engineering.
Q: Can you reuse resin?
A: Yes, but always filter resin through a fine mesh after printing to remove cured particles. Store in an opaque container away from light/heat.
Q: How strong is resin compared to filament?
A: Engineering resins like ResinMax and CeramicTough rival or exceed PLA/ABS in tensile and flexural strength.
Q: What is the shelf life of resin?
A: Most resins last 24 months unopened; once opened, use within 6 months.
7. Internal Links for SEO
Throughout the post, link strategically:
- Dental applications → Dental Category Page
- Jewelry burnout → Jewelry Category Page
- Engineering strength → Engineering Category Page
- Individual mentions (BasePro, CrownPro, WaxCast, ResinMax) → product pages
8. Conclusion
Resin 3D printing is no longer limited to hobbyists—it’s now powering breakthroughs in dentistry, jewelry, and engineering. By mastering preparation, printing, cleaning, curing, and safety, you can achieve reliable results every time.
👉 Explore our full range of Resinify 3D Printing Resins to find the right material for your next project.